Table of contents
- What is Carbon Farming?
- Why is Carbon Farming Important in India?
- Techniques Used in Carbon Farming
- Benefits of Carbon Farming
- Challenges in Carbon Farming
- Carbon Credits: How Farmers Earn Money
- Where is Carbon Farming Practised in India?
- Real Business Examples from India
- Carbon Farming vs Conventional Farming
- Future of Carbon Farming in India
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Carbon farming is a climate-smart agricultural method that helps farmers reduce greenhouse gases and earn extra income by trapping carbon in the soil. Though still new to many in India, this practice can transform both the environment and rural livelihoods.
What is Carbon Farming?
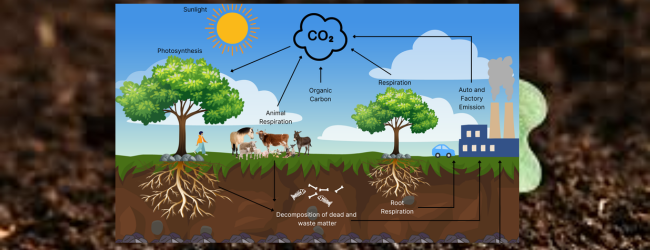
Carbon farming involves using agricultural practices that capture and store atmospheric carbon dioxide in soil and vegetation.
Detailed Info:
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a major greenhouse gas.
- Plants absorb CO2 during photosynthesis and store it in roots, stems, and soil.
- Farmers can earn carbon credits for sequestering CO2 and sell these on the carbon market.
Why is Carbon Farming Important in India?
India faces both high carbon emissions and stressed agricultural soil. Carbon farming addresses both issues.
Reasons:
- Over 55% of Indian soil is carbon-deficient (Source: ICAR).
- Agriculture contributes to 17% of India’s greenhouse gas emissions.
- Rural income diversification is critical.
Techniques Used in Carbon Farming

Different techniques help trap carbon in soil and plants.
Key Methods:
- Agroforestry: Planting trees among crops to store carbon in biomass.
- Cover Cropping: Growing non-cash crops to protect soil and trap carbon.
- Reduced Tillage: Minimal soil disturbance helps retain organic matter.
- Composting & Organic Farming: Enhances soil carbon levels.
- Biochar Application: Charred organic material added to soil increases carbon storage.
- Crop Rotation & Multicropping: Enhances biodiversity and improves soil health.
Benefits of Carbon Farming
Carbon farming benefits farmers, the environment, and the economy.
Major Benefits:
- Improved Soil Fertility
- Reduced Chemical Usage
- Higher Water Retention in Soil
- Income from Carbon Credits
- Enhanced Biodiversity
Example: A farmer in Madhya Pradesh earned Rs. 1.2 lakh in a year by selling carbon credits after implementing agroforestry.
Challenges in Carbon Farming
Adoption barriers and technical issues limit the spread.
Key Challenges:
- Lack of Awareness
- Complexity in Measuring Sequestration
- High Initial Cost of Transition
- Delayed Returns on Investment
- Limited Access to Carbon Credit Markets
Carbon Credits: How Farmers Earn Money
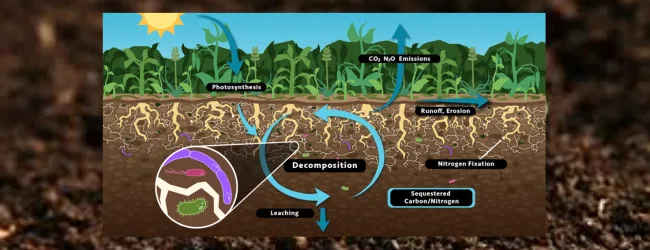
Carbon credits are tradable certificates earned for reducing carbon emissions.
How it Works:
| Activity | Carbon Stored (in tons/year) | Income (INR/ton) |
|---|---|---|
| Agroforestry (1 acre) | 2-3 | 1000-1500 |
| Cover cropping | 1-1.5 | 800-1200 |
| Biochar use | 1 | 900 |
- Credits are sold via platforms like VERRA or Gold Standard.
- NGOs and carbon finance companies assist in verification.
💡 Pro Tip: If you want to start a Business but have too many doubts, connect with a Business expert from Boss Wallah for guidance – Check Out
Where is Carbon Farming Practised in India?
Still in early stages but gaining traction in pilot projects.
Active Regions:
- Madhya Pradesh: Agroforestry pilots supported by NGOs
- Andhra Pradesh: Natural farming combined with carbon sequestration
- Punjab & Haryana: Crop residue management for emissions control
- Karnataka: Farmers trying biochar and composting methods
Real Business Examples from India
Some Indian ventures are supporting carbon farming actively.
Key Examples:
- Grow Indigo: Works with over 30,000 farmers on soil carbon improvement.
- Boomitra: Uses AI and satellite data to monitor carbon sequestration.
- CultiBio: Sells organic compost and supports carbon farming training.
Highlight: Grow Indigo helped farmers in Maharashtra earn up to Rs. 1,50,000 from carbon credits in one season.
ALSO READ | Commercial Grain Farming: A Complete Guide (2025)
Carbon Farming vs Conventional Farming
| Parameter | Carbon Farming | Conventional Farming |
| Focus | Environmental & Economic | Purely Economic |
| Soil Health | Improves Organic Carbon | Depletes Over Time |
| Inputs Used | Natural & Organic | Chemical Fertilizers |
| Profit Sources | Crop + Carbon Credit | Only Crop Yield |
| Long-Term Benefit | High | Medium to Low |
ALSO READ | Multilayer Farming: A Comprehensive Guide
Future of Carbon Farming in India
Carbon farming aligns with India’s sustainability and income goals.
Growth Drivers:
- India aims for net-zero emissions by 2070.
- The government. Promoting Natural and Organic Farming.
- Interest from carbon credit buyers globally.
Potential:
- It could cover 30 million hectares of farmland by 2030.
- The estimated market size of Rs. 20,000 crores by 2027.
Need Expert Guidance?
Starting a business can be challenging, but you don’t have to do it alone! At Boss Wallah, our 2,000+ business experts are ready to provide valuable insights and guidance. Whether you need help with marketing, finance, sourcing, or any other area of any business, our business experts are here to help you succeed
Confused about Which Business to Start?
Want to start your own business but unsure which one to choose? Explore Boss Wallah, where you’ll find 500+ courses by successful business owners, featuring practical, step-by-step guides on starting and growing various businesses.
Find your perfect business idea today
Conclusion
Carbon farming offers Indian farmers a golden opportunity to boost income while healing the planet. With government support, better awareness, and new technologies, it can become a game-changer for sustainable agriculture in India.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is carbon farming?
It’s a method of trapping carbon in soil and vegetation using farming practices.
2. Can small farmers do carbon farming?
Yes, especially with the help of NGOs and cooperatives.
3. How do I earn money from carbon farming?
By earning and selling carbon credits on verified platforms.
4. Is carbon farming profitable?
Yes, it provides long-term income through improved yields and credits.
5. What crops are best for carbon farming?
Millets, legumes, and trees like neem or moringa.
6. Do I need certification for carbon credits?
Yes, platforms like VERRA require validation.
7. What is the cost to start carbon farming?
Initial investment varies from Rs. 10,000 to Rs. 50,000 per acre.
8. Where can I get training in carbon farming?
ICAR, NGOs, and state agriculture universities offer programs.
9. Is carbon farming organic?
Not always, but it often overlaps with organic practices.
10. What are carbon offsets?
These are reductions in emissions that compensate for emissions elsewhere.


